Link budget calculations give the loss in the signal strength on the path between the mobile station antenna and base
station antenna. These calculations help in defining the cell ranges along with the coverage thresholds. Coverage
threshold is a downlink power budget that gives the signal strength at the cell edge (border of the cell) for a given
location probability.
Link budget calculations are done for both the uplink and downlink. As the power transmitted by the mobile station antenna is less than the power transmitted by the base station antenna, the uplink power budget is more critical than the downlink power budget.
Thus, the sensitivity of the base station in the uplink direction becomes one of the critical factors as it is related to reception of the power transmitted by the mobile station antenna.
In the downlink direction, transmitted power and the gains of the antennas are important parameters. In terms of losses in the equipment, the combiner loss and the cable loss are to be considered. Combiner loss comes only in the downlink calculations while the cable loss has to be incorporated in both directions.
For the other equipment (i.e. the MS), the transmitted power in the uplink direction is very important. To receive the signal transmitted from the BTS antenna even in remote areas, the sensitivity of the MS comes into play. The transmitting and the receiving antenna gains and the cable loss parameters are to be considered on the BTS side.
Character of position that we install Base Station
Logd = [Path loss - (69.55+26.16*logfc) + 13.82*loghb + a(hm)] / (44.9 - 6.55*loghb)
Allowable Path loss (Uplink) = 142.66 dB
- Base Station transmitting distance (BS)
Allowable Path loss (downlink) 141.97dB
Logd = [141.97 - (69.55+26.16log900) + 13.82log26 + 0.016] / (44.9 – 6.55log26) = 0.6240
So Distance for Base Station transmitting d(BS) = 2.66km
By the way we can study for signal reception of Mobile Station which depends on the environmental place of Mobile Station.For this case we're discussing transmitting of Base Station Path loss (Downlink) Effective isotropic radiated power(EIRP)=55.35dB
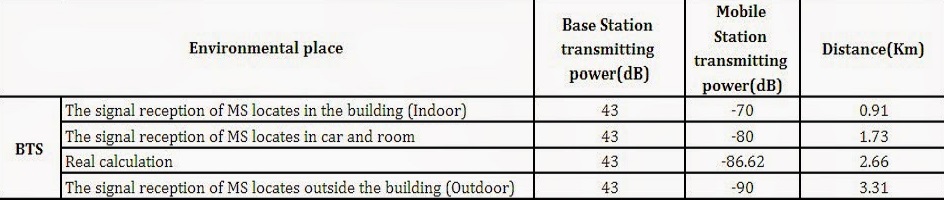
The signal reception of MS locates in the building (Indoor)
We get Path loss = EIRP - Prmin(MS) = 55.35 - (-70) = 125.35 dB
Logd = [125.35 - (69.55+26.16log900) + 13.82log26 + 0.016] / (44.9 - 6.55log26)= -0.0404
So Distance for Base Station transmitting d(BS) = 0.91km
The signal reception of MS locates in car and room
We get Path loss = EIRP - Prmin(MS) = 55.35 - (-80) = 135.35 dB
Logd = [135.35 - (69.55+26.16log900) + 13.82log26 + 0.016] / (44.9 - 6.55log26) = 0.2402
So Distance for Base Station transmitting d(BS) = 1.73km
The signal reception of MS locates outside the building (Outdoor)
We get Path loss = EIRP - Prmin(MS) = 55.35 - (-90) = 145.35 dB
Logd = [145.35 - (69.55+26.16log900) + 13.82log26 + 0.016] / (44.9 - 6.55log26) = 0.5208
So Distance for Base Station transmitting d(BS) = 3.31km
All coverage calculation relate to cell site configuration: Omnidirectional Cell, 3 Sector or 6 Sector Cell and 2 Sector Cell.
In summary table we get d(BS) from calculation: 2.66Km.
A = 2.598 x d x d = 2.598 x 2.66 x 2.66 = 18.38 Km2
A = 1.949 x d x d = 1.949 x 2.66 x 2.66 = 13.79 Km2
L = 2 x d = 2 x 2.66 = 5.32Km
We suppose one province that there are beautiful beach in our country:
Basic Number of Base Station = 826/13.79 = 59 BS
How to calculate GSM Link Budget Base Station Subsystem in Radio Network Planning?
As the link budget calculations basically include the power transmission between the base station (including the RF antenna) and the mobile station antenna, we shall look into the characteristics of these two pieces of equipment from the link budget perspective.Link budget calculations are done for both the uplink and downlink. As the power transmitted by the mobile station antenna is less than the power transmitted by the base station antenna, the uplink power budget is more critical than the downlink power budget.
Thus, the sensitivity of the base station in the uplink direction becomes one of the critical factors as it is related to reception of the power transmitted by the mobile station antenna.
In the downlink direction, transmitted power and the gains of the antennas are important parameters. In terms of losses in the equipment, the combiner loss and the cable loss are to be considered. Combiner loss comes only in the downlink calculations while the cable loss has to be incorporated in both directions.
For the other equipment (i.e. the MS), the transmitted power in the uplink direction is very important. To receive the signal transmitted from the BTS antenna even in remote areas, the sensitivity of the MS comes into play. The transmitting and the receiving antenna gains and the cable loss parameters are to be considered on the BTS side.
Base on Okumara-Hata model is the most commonly used model for macro-cell coverage planning. It is used for the frequency ranges 150-1000 MHz and 1500-2000 MHz and this model depends on two variables Antenna height and frequency. It is applied with GSM for macro cell in three location type: Typical Urban,Typical Suburban and rural. The range of calculation is from 1 to 20 km. The loss between the transmitting and receiving stations is given as:
1/ Typical Urban
where isPath loss = 69.55 + 26.16logfc + (44.9 – 6.55loghb) logd – 13.82loghb – a(hm)(dB)
- fc the frequency (MHz),
- hb is the BTS antenna height (m),
- hm is the mobile antenna height (m)
- a(hm) is a function of the MS antenna height,
- d is the distance between the BS and MS (km), and
- a(hm)match to size of city and given by:
For Small and medium-sized cities
- a(hm) = [1.1log(fc) – 0.7]hm – [1.56log(fc) – 0.8]
For large cities
- a(hm) = 8.29[log(1.54hm)]2 – 11 fc smaller than 200MHz
- a(hm) = 3.2[log(11.75hm)]2 – 4.97 fc bigger than 400Mhz
2/ Typical Suburban
Path loss = Path loss (Urban) – 2[9log(fc/28)2) – 5.4] (dB)
3/ Rural
Path loss = Path loss (Urban) – 4.78(logfc)2+ 18.33logfc – 40.94 (dB)
- Antenna Type: APX906515L-T0-0
- Antenna height: 26m
- Region: urban and suburban
- Feeder Type: HFC22D(A)LS Cable 2006
- Feeder loss: 3.71dB per 100m
- Feeder length: 46m
- Allowable Path loss (uplink) 142.66dB
- Allowable Path loss (downlink) 141.97dB (Allowable pathloss)
- 150 ≤ fc ≤ 2200 MHz
- 30 ≤ hb ≤ 200 m
- 1 ≤ hm ≤ 10 m
- 1 ≤ d ≤20 Km
We study case Urban
Path loss = 69.55 + 26.16logfc + (44.9 – 6.55loghb) logd – 13.82loghb– a(hm)(dB)
I determine that the region is small.
- a(hm) = [1.1log(fc) – 0.7]hm – [1.56log(fc) – 0.8]
- hm=1.5m
- fc =900MHz
- a(hm) = [1.1*log(900)-0.7]*1.5 - [1.56*log(900)-0.8]= 0.016dB
Base Station Coverage
- Mobile transmitting distance (MS)Logd = [Path loss - (69.55+26.16*logfc) + 13.82*loghb + a(hm)] / (44.9 - 6.55*loghb)
Allowable Path loss (Uplink) = 142.66 dB
Logd = [142.66 - (69.55+26.16log900) + 13.82log26 + 0.016] / (44.9 – 6.55log26) = 0.4454
So Distance for mobile transmitting d(MS) = 2.78km
- Base Station transmitting distance (BS)
Allowable Path loss (downlink) 141.97dB
Logd = [141.97 - (69.55+26.16log900) + 13.82log26 + 0.016] / (44.9 – 6.55log26) = 0.6240
So Distance for Base Station transmitting d(BS) = 2.66km
By the way we can study for signal reception of Mobile Station which depends on the environmental place of Mobile Station.For this case we're discussing transmitting of Base Station Path loss (Downlink) Effective isotropic radiated power(EIRP)=55.35dB
1/ Case1: Prmin(MS)= -70dB
The signal reception of MS locates in the building (Indoor)
We get Path loss = EIRP - Prmin(MS) = 55.35 - (-70) = 125.35 dB
Logd = [125.35 - (69.55+26.16log900) + 13.82log26 + 0.016] / (44.9 - 6.55log26)= -0.0404
So Distance for Base Station transmitting d(BS) = 0.91km
2/ Case2: Prmin(MS)= -80dB
The signal reception of MS locates in car and room
We get Path loss = EIRP - Prmin(MS) = 55.35 - (-80) = 135.35 dB
Logd = [135.35 - (69.55+26.16log900) + 13.82log26 + 0.016] / (44.9 - 6.55log26) = 0.2402
So Distance for Base Station transmitting d(BS) = 1.73km
3/ Case3: Prmin(MS)= -90dB
The signal reception of MS locates outside the building (Outdoor)
We get Path loss = EIRP - Prmin(MS) = 55.35 - (-90) = 145.35 dB
Logd = [145.35 - (69.55+26.16log900) + 13.82log26 + 0.016] / (44.9 - 6.55log26) = 0.5208
So Distance for Base Station transmitting d(BS) = 3.31km
Coverage Calculation
All coverage calculation relate to cell site configuration: Omnidirectional Cell, 3 Sector or 6 Sector Cell and 2 Sector Cell.
In summary table we get d(BS) from calculation: 2.66Km.
- Omnidirectional Cell
A = 2.598 x d x d = 2.598 x 2.66 x 2.66 = 18.38 Km2
- 3 Sector or 6 Sector Cell
A = 1.949 x d x d = 1.949 x 2.66 x 2.66 = 13.79 Km2
- 2 Sector Cell
L = 2 x d = 2 x 2.66 = 5.32Km
We suppose one province that there are beautiful beach in our country:
- Population; 164779
- Number people per Km2: 179
- Surface area: 826Km2
Basic Number of Base Station = 826/13.79 = 59 BS
Note: Number of BSs depend on actual requirement of users in area so it can be less or more than theory calculation.

Great explanation of GSM link budget and coverage! The step-by-step Okumura-Hata model examples make it easy to understand real-world scenarios. For those who like exploring tech beyond telecom, flipper unleashed is another fascinating project.
ReplyDeletePost a Comment