The production system design planning considers input requirements, conversion process and output. After considering the forecast and long-term planning organization should undertake capacity planning.
Capacity is defined as the ability to achieve, store or produce. For an organization, capacity would be the ability of a given system to produce output within the specific time period. In operations, management capacity is referred as an amount of the input resources available to produce relative output over period of time.
In general, terms capacity is referred as maximum production capacity, which can be attained within a normal working schedule.
Capacity planning is essential to be determining optimum utilization of resource and plays an important role decision-making process, for example, extension of existing operations, modification to product lines, starting new products, etc. Strategic Capacity Planning
A technique used to identify and measure overall capacity of production is referred to as strategic capacity planning. Strategic capacity planning is utilized for capital intensive resource like plant, machinery, labor, etc.
Strategic capacity planning is essential as it helps the organization in meeting the future requirements of the organization. Planning ensures that operating cost are maintained at a minimum possible level without affecting the quality. It ensures the organization remain competitive and can achieve the long-term growth plan.
Capacity planning based on the timeline is classified into three main categories long range, medium range and short range.
Long Term Capacity: Long range capacity of an organization is dependent on various other capacities like design capacity, production capacity, sustainable capacity and effective capacity. Design capacity is the maximum output possible as indicated by equipment manufacturer under ideal working condition.
Production capacity is the maximum output possible from equipment under normal working condition or day.
Sustainable capacity is the maximum production level achievable in realistic work condition and considering normal machine breakdown, maintenance, etc.
Effective capacity is the optimum production level under pre-defined job and work-schedules, normal machine breakdown, maintenance, etc.
Medium Term Capacity: The strategic capacity planning undertaken by organization for 2 to 3 years of a time frame is referred to as medium term capacity planning.
Short Term Capacity: The strategic planning undertaken by organization for a daily weekly or quarterly time frame is referred to as short term capacity planning.
The ultimate goal of capacity planning is to meet the current and future level of the requirement at a minimal wastage. The three types of capacity planning based on goal are lead capacity planning, lag strategy planning and match strategy planning.
Effective capacity planning is dependent upon factors like production facility (layout, design, and location), product line or matrix, production technology, human capital (job design, compensation), operational structure (scheduling, quality assurance) and external structure ( policy, safety regulations)
There would be a scenario where capacity planning done on a basis of forecasting may not exactly match. For example, there could be a scenario where demand is more than production capacity; in this situation, a company needs to fulfill its requirement by buying from outside. If demand is equal to production capacity; company is in a position to use its production capacity to the fullest. If the demand is less than the production capacity, company can choose to reduce the production or share it output with other manufacturers.
Example: We assume that a location has 164779 people in urban area and base on base station calculation (GSM Network Coverage in Radio Network Planning) 59 Base Station.
To calculate TX capacity we need some parameters as below:
To determine max subscribers that Base Station support:
1. Erlang per subscriber = Average duration subscriber per customer for a month/(Day number per month * Busy hour per day * 60)
Erlang per subscriber = 180/(24*4*60) = 0.031 Erlang
2. Total Channel of RF carriers = (Allocated spectrum * 1000)/RF Channel Bandwidth( full rate)
Total Channel of RF carriers = 10*1000/200 = 50 Channels
3. Total RF carriers per cell = Total Base Station * Frequency Reuse Factor
Base on Frequency planning in GSM Network Frequency Reuse Factor : 4x3
Total RF carriers per cell = 59/(4*3) = 4 TRx
4. Traffic Channel per Cell = (Total RF carriers per cell * Time Slot per TRx) - Control Channel per cell
Traffic Channel per Cell = 4*8-2 = 30
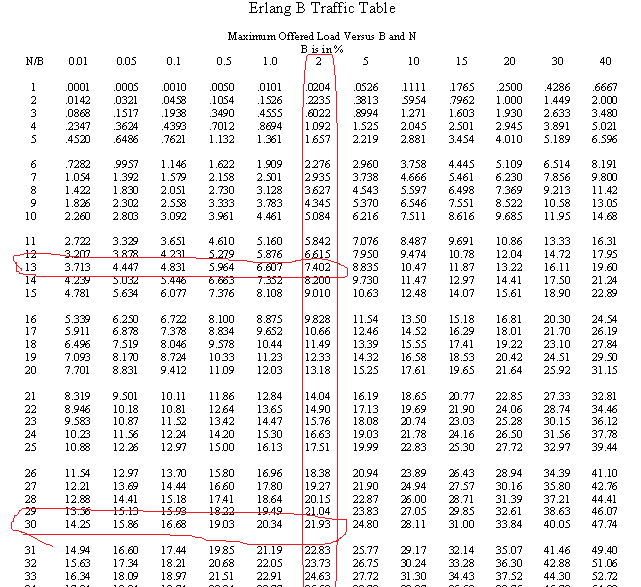
Determine Traffic Capacity of GSM network GoS = 2% refer to ErlarngB table we get Traffic Channel per cell = 30 matches to 21.93 Erlangs
5. Traffic Capacity per Base Station = Traffic Capacity * Sectors
Traffic Capacity per Base Station = 21.93 * 3 = 65.79 Erlangs
6. Max Subscriber per Base Station = Traffic Capacity per Base Station/Erlang per subscriber
Max Subscribers per Base Station = 65.79 * 0.031 = 2122 Subscribers
1. Traffic capacity volume per Cell = 250 * 0.03 = 7.5 Erlangs
2. From Erlang-B determine Channels
Traffic Capacity volume = 7.5 Erlangs matches 13 Channels
Capacity is defined as the ability to achieve, store or produce. For an organization, capacity would be the ability of a given system to produce output within the specific time period. In operations, management capacity is referred as an amount of the input resources available to produce relative output over period of time.
In general, terms capacity is referred as maximum production capacity, which can be attained within a normal working schedule.
Capacity planning is essential to be determining optimum utilization of resource and plays an important role decision-making process, for example, extension of existing operations, modification to product lines, starting new products, etc. Strategic Capacity Planning
A technique used to identify and measure overall capacity of production is referred to as strategic capacity planning. Strategic capacity planning is utilized for capital intensive resource like plant, machinery, labor, etc.
Strategic capacity planning is essential as it helps the organization in meeting the future requirements of the organization. Planning ensures that operating cost are maintained at a minimum possible level without affecting the quality. It ensures the organization remain competitive and can achieve the long-term growth plan.
Capacity Planning Classification
Capacity planning based on the timeline is classified into three main categories long range, medium range and short range.
Long Term Capacity: Long range capacity of an organization is dependent on various other capacities like design capacity, production capacity, sustainable capacity and effective capacity. Design capacity is the maximum output possible as indicated by equipment manufacturer under ideal working condition.
Production capacity is the maximum output possible from equipment under normal working condition or day.
Sustainable capacity is the maximum production level achievable in realistic work condition and considering normal machine breakdown, maintenance, etc.
Effective capacity is the optimum production level under pre-defined job and work-schedules, normal machine breakdown, maintenance, etc.
Medium Term Capacity: The strategic capacity planning undertaken by organization for 2 to 3 years of a time frame is referred to as medium term capacity planning.
Short Term Capacity: The strategic planning undertaken by organization for a daily weekly or quarterly time frame is referred to as short term capacity planning.
Goal of Capacity Planning
The ultimate goal of capacity planning is to meet the current and future level of the requirement at a minimal wastage. The three types of capacity planning based on goal are lead capacity planning, lag strategy planning and match strategy planning.
Factors Affecting Capacity Planning
Effective capacity planning is dependent upon factors like production facility (layout, design, and location), product line or matrix, production technology, human capital (job design, compensation), operational structure (scheduling, quality assurance) and external structure ( policy, safety regulations)
Forecasting v/s Capacity Planning
There would be a scenario where capacity planning done on a basis of forecasting may not exactly match. For example, there could be a scenario where demand is more than production capacity; in this situation, a company needs to fulfill its requirement by buying from outside. If demand is equal to production capacity; company is in a position to use its production capacity to the fullest. If the demand is less than the production capacity, company can choose to reduce the production or share it output with other manufacturers.
- Average duration subscriber per customer for a month : 180 mins
- Busy hour per day : 4 hours
- Day number per month : 24 days
- Allocated spectrum : 10 MHz
- Frequency Reuse : 4x3
- RF Channel Bandwidth( full rate) : 200 KHz
- Area Square : 826 Km2
- Estimate subscribers : 35000 people
- Capacity BTS equipment : BTS characteristic
- Control Channel per cell : 2
Frequency planning in GSM Network
To determine max subscribers that Base Station support:
1. Erlang per subscriber = Average duration subscriber per customer for a month/(Day number per month * Busy hour per day * 60)
Erlang per subscriber = 180/(24*4*60) = 0.031 Erlang
2. Total Channel of RF carriers = (Allocated spectrum * 1000)/RF Channel Bandwidth( full rate)
Total Channel of RF carriers = 10*1000/200 = 50 Channels
3. Total RF carriers per cell = Total Base Station * Frequency Reuse Factor
Base on Frequency planning in GSM Network Frequency Reuse Factor : 4x3
Total RF carriers per cell = 59/(4*3) = 4 TRx
4. Traffic Channel per Cell = (Total RF carriers per cell * Time Slot per TRx) - Control Channel per cell
Traffic Channel per Cell = 4*8-2 = 30
Determine Traffic Capacity of GSM network GoS = 2% refer to ErlarngB table we get Traffic Channel per cell = 30 matches to 21.93 Erlangs
5. Traffic Capacity per Base Station = Traffic Capacity * Sectors
Traffic Capacity per Base Station = 21.93 * 3 = 65.79 Erlangs
6. Max Subscriber per Base Station = Traffic Capacity per Base Station/Erlang per subscriber
Max Subscribers per Base Station = 65.79 * 0.031 = 2122 Subscribers
Referring to predict utilization of people 810 people so subscribers per cell is 250.
We suppose that Company provide Traffic Capacity per customer 0.03 Erlang and GoS 2% So we get result:
1. Traffic capacity volume per Cell = 250 * 0.03 = 7.5 Erlangs
2. From Erlang-B determine Channels
Traffic Capacity volume = 7.5 Erlangs matches 13 Channels
Due to 1TRx has 8 Channels so 13 Channels needs 2 TRXs
So Site configuration is S2/2/2
 |
| Erlang-B Table |

Post a Comment